Sizden gelen soru:
Su döngüsünün ingilizce aşamaları?
Cevap:
Su döngüsü yada su çevriminin aşamalarını aşağıda İngilizce olarak sizlere aktardık. Su döngüsünün her bir aşamasını ve bu aşamaya ait açıklamaları verdik. Ayrıca İngilizce olarak su döngüsünü resimli bir şekilde de gösterdik.
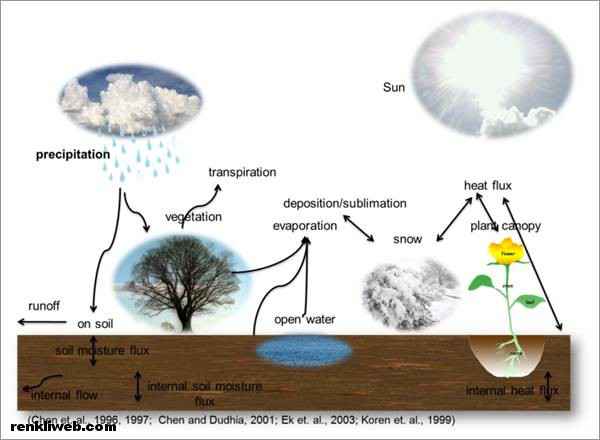
Water Cycle Processes
Precipitation
Condensed water vapor that falls to the Earth’s surface . Most precipitation occurs as rain, but also includes snow, hail, fog drip, graupel, and sleet. Approximately 505,000 km3 (121,000 cu mi) of water falls as precipitation each year, 398,000 km3 (95,000 cu mi) of it over the oceans. The rain on land contains 107,000 km3 (26,000 cu mi) of water per year and a snowing only 1,000 km3 (240 cu mi). 78% of global precipitation occurs over the ocean.
Canopy interception
The precipitation that is intercepted by plant foliage, eventually evaporates back to the atmosphere rather than falling to the ground.
Snowmelt
The runoff produced by melting snow.
Runoff
The variety of ways by which water moves across the land. This includes both surface runoff and channel runoff. As it flows, the water may seep into the ground, evaporate into the air, become stored in lakes or reservoirs, or be extracted for agricultural or other human uses.
Infiltration
The flow of water from the ground surface into the ground. Once infiltrated, the water becomes soil moisture or groundwater.
Subsurface flow
The flow of water underground, in the vadose zone and aquifers. Subsurface water may return to the surface (e.g. as a spring or by being pumped) or eventually seep into the oceans. Water returns to the land surface at lower elevation than where it infiltrated, under the force of gravity or gravity induced pressures. Groundwater tends to move slowly, and is replenished slowly, so it can remain in aquifers for thousands of years.
Evaporation
The transformation of water from liquid to gas phases as it moves from the ground or bodies of water into the overlying atmosphere. The source of energy for evaporation is primarily solar radiation. Evaporation often implicitly includes transpiration from plants, though together they are specifically referred to as evapotranspiration. Total annual evapotranspiration amounts to approximately 505,000 km3 (121,000 cu mi) of water, 434,000 km3 (104,000 cu mi) of which evaporates from the oceans. 86% of global evaporation occurs over the ocean.
Sublimation
The state change directly from solid water (snow or ice) to water vapor.
Deposition
This refers to changing of water vapor directly to ice.
Advection
The movement of water — in solid, liquid, or vapor states — through the atmosphere. Without advection, water that evaporated over the oceans could not precipitate over land.
Condensation
The transformation of water vapor to liquid water droplets in the air, creating clouds and fog.
Transpiration
The release of water vapor from plants and soil into the air. Water vapor is a gas that cannot be seen.
Percolation
Water flows horizontally through the soil and rocks under the influence of gravity
Plate tectonics
Water enters the mantle via subduction of oceanic crust. Water returns to the surface via volcanism.